A network is a linked set of computer systems which may be capable of sharing computer power and resources such as printers and databases.
Network topology:
A topology is the theoretical arrangement of components of a network.
Actual arrangements are determined by physical factors
Topologies will affect:
- Cost
-Performance
-Ease of installation
The types of topology:
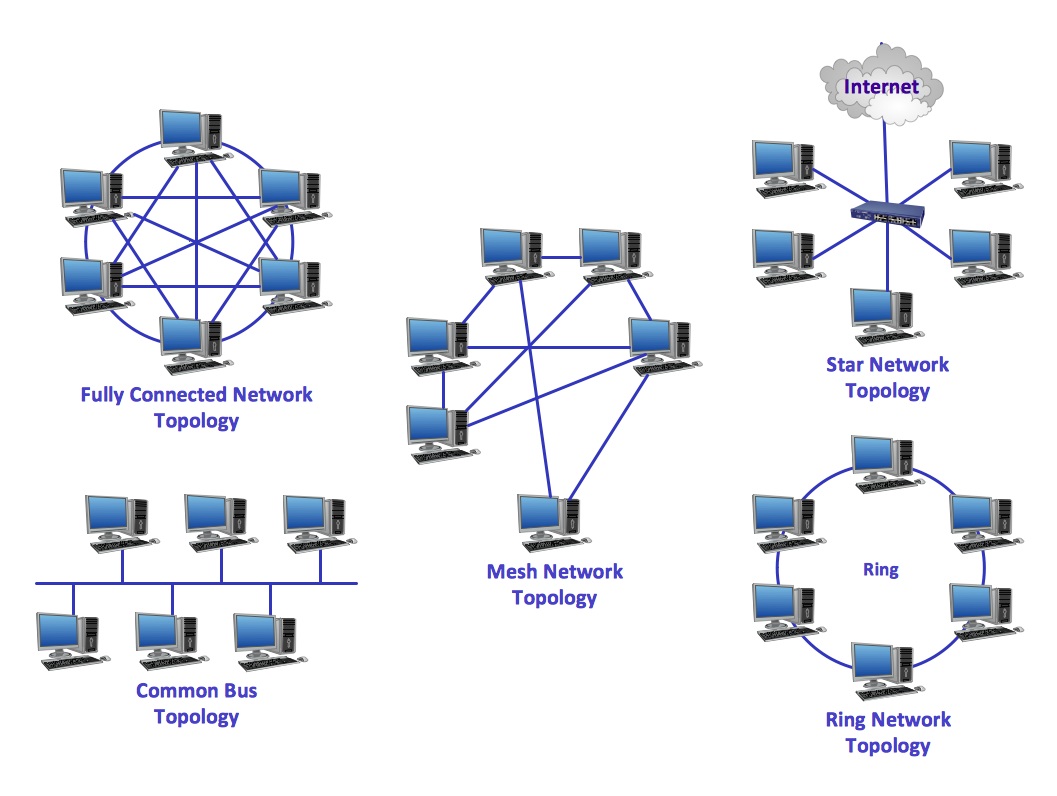
Star:
- Shared link to server(s)
- Central node is the Hub
- Few data collisions
- Fast, robust and cost effective
- Can set up independent segments
- the hub can be another node or switch
- The Hub has a separate connection to each node

Bus :
- This uses one common linking cable (bus)
- Cheapest network design
- Network will slow down when there is heavy traffic
- Network is prone to lots of data collisions
- Breakage to the bus will affect the whole network.
- Only a limited distance can be covered.
- Terminators are required for this topology, which denote the start and end point of the bus line, to detect when data has not reached its destination.

Ring:
- One direction traffic
- fast performance
- Every node is required to have a network interface controller which allows it to communicate across a network using a series of protocol.
- Data will pass through the NIC of each node

Mesh:
- Most common type of network
- Using decentralised design
- can be wired or wireless
- no single point of failure
- each node connects to 2+ other nodes
- Nodes communicate directly with one another without needing internet connection.

All Types of network topology:
LAN:
- Local Area Network
- Networked computers are located fairly near to one another geographically
- An example is all the computers in a school or office.
- Each devices is called a node.
- The entire infrastructure is owned by the organisation who own the LAN.
- All infrastructure is the responsibility and maintained by the organisation or individual
- Some equipment can be leased form external companies- in this case the companies is responsible and in control of repairing it. Usually to do with routers or wireless access points
- allows communication between workers
- allows data/files/information to be shared
- peripherals can be shared e.g. printers
- computers (software) can be updated/upgraded more easily (also virus scans)
- Log on from any connected machine
- Distributed processing where a program can be run simultaneously on may nodes
- NIC- needed to connect to a LAN, allows computer to communicate over a network by providing physical access to a network and provides a unique address for each the node, the MAC (Media Access Control) address.
- Router:
- forwards data packets across many networks so are different to switches. They reseieve packets read the address information and use a routing table to forward thje packet to the next network
- Switch:
- Allows network segments to be created and reduces data collisions and is hardware within the network for internal communication, a router forwards data packets across many networks so are different
- Allows wireless devices to connect to a wired network
- uses WI-FI, Bluetooth or related standards
- Usually connects to a router via a wired network.
- can relay data between the wireless and wired data
WAN:
- Wide area Network
- Computers are located in various distant locations geographically
- WAN is the result of joining two or more geographically separate LANs via satellite, fibre-optic cables, telephone lines or a combination of these.
- The infrastructure may be provided by telecoms companies.
- The largest WAN in existence is the Internet.#
SAN:
- Storage Area Network
- Dedicated network used for large scale storage of data in data centres.
- Common uses of a SAN include email servers, databases, and high usage file servers
PAN:
- Personal Area Network
- Used for data transmission among devices such as computers, smartphones & tablets. Can be used for communication between personal devices or to connect to a higher level network and / or Internet.
The Cloud:
- Data storage and services moved off site
- 3rd party manages maintenance, security, backups etc.
Advantages:
– No in-house maintenance
– Cheaper (less staff)
Disadvantages:
–loss of control / Security
–Relies on an internet connection

No comments:
Post a Comment